What Do Home Inspectors Check?
A complete Home Inspection List
Purpose of a home inspection
A general home inspection is a non-invasive, visual examination of the accessible areas of a residential property (as delineated below), performed for a fee, which is designed to identify defects within specific systems and components defined by these Standards that are both observed and deemed material by the inspector. The scope of work may be modified by the Client and Inspector prior to the inspection process.
1.3. A general home inspection report shall identify, in written format, defects within specific systems and components defined by these Standards that are both observed and deemed material by the inspector. Inspection reports may include additional comments and recommendations.
- The general home inspection is based on the observations made on the date of the inspection, and not a prediction of future conditions.
- The general home inspection will not reveal every issue that exists or ever could exist, but only those material defects observed on the date of the inspection.
1.3. A general home inspection report shall identify, in written format, defects within specific systems and components defined by these Standards that are both observed and deemed material by the inspector. Inspection reports may include additional comments and recommendations.
Roof
I. The inspector shall inspect from ground level or the eaves:
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- the roof-covering materials;
- the gutters;
- the downspouts;
- the vents, flashing, skylights, chimney, and other roof penetrations; and
- the general structure of the roof from the readily accessible panels, doors or stairs.
- the type of roof-covering materials.
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- observed indications of active roof leaks.
- walk on any roof surface.
- predict the service life expectancy.
- inspect underground downspout diverter drainage pipes.
- remove snow, ice, debris or other conditions that prohibit the observation of the roof surfaces.
- move insulation.
- inspect antennae, satellite dishes, lightning arresters, de-icing equipment, or similar attachments.
- walk on any roof areas that appear, in the inspector's opinion, to be unsafe.
- walk on any roof areas if doing so might, in the inspector's opinion, cause damage.
- perform a water test.
- warrant or certify the roof.
- confirm proper fastening or installation of any roof-covering material.
Exterior
I. The inspector shall inspect:
II. The inspector shall describe:
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- the exterior wall-covering materials;
- the eaves, soffits and fascia;
- a representative number of windows;
- all exterior doors;
- flashing and trim;
- adjacent walkways and driveways;
- stairs, steps, stoops, stairways and ramps;
- porches, patios, decks, balconies and carports;
- railings, guards and handrails; and
- vegetation, surface drainage, retaining walls and grading of the property, where they may adversely affect the structure due to moisture intrusion.
II. The inspector shall describe:
- the type of exterior wall-covering materials.
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- any improper spacing between intermediate balusters, spindles and rails.
- inspect or operate screens, storm windows, shutters, awnings, fences, outbuildings, or exterior accent lighting.
- inspect items that are not visible or readily accessible from the ground, including window and door flashing.
- inspect or identify geological, geotechnical, hydrological or soil conditions.
- inspect recreational facilities or playground equipment.
- inspect seawalls, breakwalls or docks.
- inspect erosion-control or earth-stabilization measures.
- inspect for safety-type glass.
- inspect underground utilities.
- inspect underground items.
- inspect wells or springs.
- inspect solar, wind or geothermal systems.
- inspect swimming pools or spas.
- inspect wastewater treatment systems, septic systems or cesspools.
- inspect irrigation or sprinkler systems.
- inspect drainfields or dry wells.
- determine the integrity of multiple-pane window glazing or thermal window seals.
Basement, foundation, crawlspace and structure
I. The inspector shall inspect:
- the foundation;
- the basement;
- the crawlspace; and
- structural components.
- the type of foundation; and
- the location of the access to the under-floor space.
- observed indications of wood in contact with or near soil;
- observed indications of active water penetration;
- observed indications of possible foundation movement, such as sheetrock cracks, brick cracks, out-of-square door frames, and unlevel floors; and
- any observed cutting, notching and boring of framing members that may, in the inspector's opinion, present a structural or safety concern.
- enter any crawlspace that is not readily accessible, or where entry could cause damage or pose a hazard to him/herself.
- move stored items or debris.
- operate sump pumps with inaccessible floats.
- identify the size, spacing, span or location or determine the adequacy of foundation bolting, bracing, joists, joist spans or support systems.
- provide any engineering or architectural service.
- report on the adequacy of any structural system or component.
Heating
I. The inspector shall inspect:
- the heating system, using normal operating controls.
- the location of the thermostat for the heating system;
- the energy source; and
- the heating method.
- any heating system that did not operate; and
- if the heating system was deemed inaccessible.
- inspect, measure, or evaluate the interior of flues or chimneys, fire chambers, heat exchangers, combustion air systems, fresh-air intakes, makeup air, humidifiers, dehumidifiers, electronic air filters, geothermal systems, or solar heating systems.
- inspect fuel tanks or underground or concealed fuel supply systems.
- determine the uniformity, temperature, flow, balance, distribution, size, capacity, BTU, or supply adequacy of the heating system.
- light or ignite pilot flames.
- activate heating, heat pump systems, or other heating systems when ambient temperatures or other circumstances are not conducive to safe operation or may damage the equipment.
- override electronic thermostats.
- evaluate fuel quality.
- verify thermostat calibration, heat anticipation, or automatic setbacks, timers, programs or clocks.
- measure or calculate the air for combustion, ventilation, or dilution of flue gases for appliances.
Cooling
I. The inspector shall inspect:
- the cooling system, using normal operating controls.
- the location of the thermostat for the cooling system; and
- the cooling method.
- any cooling system that did not operate; and
- if the cooling system was deemed inaccessible.
- determine the uniformity, temperature, flow, balance, distribution, size, capacity, BTU, or supply adequacy of the cooling system.
- inspect portable window units, through-wall units, or electronic air filters.
- operate equipment or systems if the exterior temperature is below 65° Fahrenheit, or when other circumstances are not conducive to safe operation or may damage the equipment.
- inspect or determine thermostat calibration, cooling anticipation, or automatic setbacks or clocks.
- examine electrical current, coolant fluids or gases, or coolant leakage.
Plumbing
I. The inspector shall inspect:
- the main water supply shut-off valve;
- the main fuel supply shut-off valve;
- the water heating equipment, including the energy source, venting connections, temperature/pressure-relief (TPR) valves, Watts 210 valves, and seismic bracing;
- interior water supply, including all fixtures and faucets, by running the water;
- all toilets for proper operation by flushing;
- all sinks, tubs and showers for functional drainage;
- the drain, waste and vent system; and
- drainage sump pumps with accessible floats.
- whether the water supply is public or private based upon observed evidence;
- the location of the main water supply shut-off valve;
- the location of the main fuel supply shut-off valve;
- the location of any observed fuel-storage system; and
- the capacity of the water heating equipment, if labeled.
- deficiencies in the water supply by viewing the functional flow in two fixtures operated simultaneously;
- deficiencies in the installation of hot and cold water faucets;
- mechanical drain stops that were missing or did not operate if installed in sinks, lavatories and tubs; and
- toilets that were damaged, had loose connections to the floor, were leaking, or had tank components that did not operate.
- light or ignite pilot flames.
- measure the capacity, temperature, age, life expectancy or adequacy of the water heater.
- inspect the interior of flues or chimneys, combustion air systems, water softener or filtering systems, well pumps or tanks, safety or shut-off valves, floor drains, lawn sprinkler systems, or fire sprinkler systems.
- determine the exact flow rate, volume, pressure, temperature or adequacy of the water supply.
- determine the water quality, potability or reliability of the water supply or source.
- open sealed plumbing access panels.
- inspect clothes washing machines or their connections.
- operate any valve.
- test shower pans, tub and shower surrounds or enclosures for leakage or functional overflow protection.
- evaluate the compliance with conservation, energy or building standards, or the proper design or sizing of any water, waste or venting components, fixtures or piping.
- determine the effectiveness of anti-siphon, back-flow prevention or drain-stop devices.
- determine whether there are sufficient cleanouts for effective cleaning of drains.
- evaluate fuel storage tanks or supply systems.
- inspect wastewater treatment systems.
- inspect water treatment systems or water filters.
- inspect water storage tanks, pressure pumps, or bladder tanks.
- evaluate wait time to obtain hot water at fixtures, or perform testing of any kind to water heater elements.
- evaluate or determine the adequacy of combustion air.
- test, operate, open or close: safety controls, manual stop valves, temperature/pressure-relief valves, control valves, or check valves.
- examine ancillary or auxiliary systems or components, such as, but not limited to, those related to solar water heating and hot water circulation.
- determine the existence or condition of polybutylene, polyethylene, or similar plastic piping.
- inspect or test for gas or fuel leaks, or indications thereof.
electrical
I. The inspector shall inspect:
II. The inspector shall describe:
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- the service drop;
- the overhead service conductors and attachment point;
- the service head, gooseneck and drip loops;
- the service mast, service conduit and raceway;
- the electric meter and base;
- service-entrance conductors;
- the main service disconnect;
- panelboards and over-current protection devices (circuit breakers and fuses);
- service grounding and bonding;
- a representative number of switches, lighting fixtures and receptacles, including receptacles observed and deemed to be arc-fault circuit interrupter (AFCI)-protected using the AFCI test button, where possible;
- all ground-fault circuit interrupter receptacles and circuit breakers observed and deemed to be GFCIs using a GFCI tester, where possible; and
- for the presence of smoke and carbon-monoxide detectors.
II. The inspector shall describe:
- the main service disconnect's amperage rating, if labeled; and
- the type of wiring observed.
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- deficiencies in the integrity of the service-entrance conductors’ insulation, drip loop, and vertical clearances from grade and roofs;
- any unused circuit-breaker panel opening that was not filled;
- the presence of solid conductor aluminum branch-circuit wiring, if readily visible;
- any tested receptacle in which power was not present, polarity was incorrect, the cover was not in place, the GFCI devices were not properly installed or did not operate properly, evidence of arcing or excessive heat, and where the receptacle was not grounded or was not secured to the wall; and
- the absence of smoke and/or carbon monoxide detectors.
- insert any tool, probe or device into the main panelboard, sub-panels, distribution panelboards, or electrical fixtures.
- operate electrical systems that are shut down.
- remove panelboard cabinet covers or dead fronts.
- operate or re-set over-current protection devices or overload devices.
- operate or test smoke or carbon-monoxide detectors or alarms.
- inspect, operate or test any security, fire or alarm systems or components, or other warning or signaling systems.
- measure or determine the amperage or voltage of the main service equipment, if not visibly labeled.
- inspect ancillary wiring or remote-control devices.
- activate any electrical systems or branch circuits that are not energized.
- inspect low-voltage systems, electrical de-icing tapes, swimming pool wiring, or any time-controlled devices.
- verify the service ground.
- inspect private or emergency electrical supply sources, including, but not limited to: generators, windmills, photovoltaic solar collectors, or battery or electrical storage facility.
- inspect spark or lightning arrestors.
- inspect or test de-icing equipment.
- conduct voltage-drop calculations.
- determine the accuracy of labeling.
- inspect exterior lighting.
fireplace
I. The inspector shall inspect:
II. The inspector shall describe:
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- readily accessible and visible portions of the fireplaces and chimneys;
- lintels above the fireplace openings;
- damper doors by opening and closing them, if readily accessible and manually operable; and
- cleanout doors and frames.
II. The inspector shall describe:
- the type of fireplace.
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- evidence of joint separation, damage or deterioration of the hearth, hearth extension or chambers;
- manually operated dampers that did not open and close;
- the lack of a smoke detector in the same room as the fireplace;
- the lack of a carbon-monoxide detector in the same room as the fireplace; and
- cleanouts not made of metal, pre-cast cement, or other non-combustible material.
- inspect the flue or vent system.
- inspect the interior of chimneys or flues, fire doors or screens, seals or gaskets, or mantels.
- determine the need for a chimney sweep.
- operate gas fireplace inserts.
- light pilot flames.
- determine the appropriateness of any installation.
- inspect automatic fuel-fed devices.
- inspect combustion and/or make-up air devices.
- inspect heat-distribution assists, whether gravity-controlled or fan-assisted.
- ignite or extinguish fires.
- determine the adequacy of drafts or draft characteristics.
- move fireplace inserts, stoves or firebox contents.
- perform a smoke test.
- dismantle or remove any component.
- perform a National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)-style inspection.
- perform a Phase I fireplace and chimney inspection.
Attic, insulation and ventilation
I. The inspector shall inspect:
II. The inspector shall describe:
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- insulation in unfinished spaces, including attics, crawlspaces and foundation areas;
- ventilation of unfinished spaces, including attics, crawlspaces and foundation areas; and
- mechanical exhaust systems in the kitchen, bathrooms and laundry area.
II. The inspector shall describe:
- the type of insulation observed; and
- the approximate average depth of insulation observed at the unfinished attic floor area or roof structure.
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- the general absence of insulation or ventilation in unfinished spaces.
- enter the attic or any unfinished spaces that are not readily accessible, or where entry could cause damage or, in the inspector's opinion, pose a safety hazard.
- move, touch or disturb insulation.
- move, touch or disturb vapor retarders.
- break or otherwise damage the surface finish or weather seal on or around access panels or covers.
- identify the composition or R-value of insulation material.
- activate thermostatically operated fans.
- determine the types of materials used in insulation or wrapping of pipes, ducts, jackets, boilers or wiring.
- determine the adequacy of ventilation.
Doors, windows and interior
I. The inspector shall inspect:
II. The inspector shall describe:
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- a representative number of doors and windows by opening and closing them;
- floors, walls and ceilings;
- stairs, steps, landings, stairways and ramps;
- railings, guards and handrails; and
- garage vehicle doors and the operation of garage vehicle door openers, using normal operating controls.
II. The inspector shall describe:
- a garage vehicle door as manually-operated or installed with a garage door opener.
III. The inspector shall report as in need of correction:
- improper spacing between intermediate balusters, spindles and rails for steps, stairways, guards and railings;
- photo-electric safety sensors that did not operate properly; and
- any window that was obviously fogged or displayed other evidence of broken seals.
- inspect paint, wallpaper, window treatments or finish treatments.
- inspect floor coverings or carpeting.
- inspect central vacuum systems.
- inspect for safety glazing.
- inspect security systems or components.
- evaluate the fastening of islands, countertops, cabinets, sink tops or fixtures.
- move furniture, stored items, or any coverings, such as carpets or rugs, in order to inspect the concealed floor structure.
- move suspended-ceiling tiles.
- inspect or move any household appliances.
- inspect or operate equipment housed in the garage, except as otherwise noted.
- verify or certify the proper operation of any pressure-activated auto-reverse or related safety feature of a garage door.
- operate or evaluate any security bar release and opening mechanisms, whether interior or exterior, including their compliance with local, state or federal standards.
- operate any system, appliance or component that requires the use of special keys, codes, combinations or devices.
- operate or evaluate self-cleaning oven cycles, tilt guards/latches, or signal lights.
- inspect microwave ovens or test leakage from microwave ovens.
- operate or examine any sauna, steam-generating equipment, kiln, toaster, ice maker, coffee maker, can opener, bread warmer, blender, instant hot-water dispenser, or other small, ancillary appliances or devices.
- inspect elevators.
- inspect remote controls.
- inspect appliances.
- inspect items not permanently installed.
- discover firewall compromises.
- inspect pools, spas or fountains.
- determine the adequacy of whirlpool or spa jets, water force, or bubble effects.
- determine the structural integrity or leakage of pools or spas.
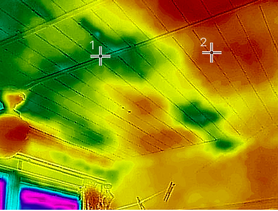
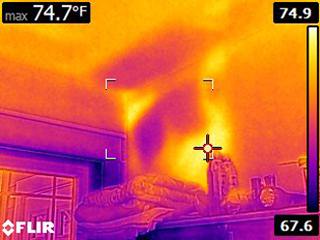
You can't report what you can't see
-Why We Offer Free Infrared Imaging
MoistureInfrared imaging can help identify moisture such as leaking pipes, failing roofs and mold hidden behind walls and flooring.
|
ElectricalFailing electrical outlets and over heated circuits give off a lot of heat that can be seen with an infrared camera.
|
EnergyInfrared imaging helps to quickly identify missing insulation, leaking windows and other areas of concern that will increase your energy bill.
|